Duboscquella tintinnicola
Diagnosis
Diagnosis_Genus: Duboscquella Chatton, 1920, emend. Coats & Bachvaroff 2012. Duboscquellidae ectoparasitic on tintinnids. Trophont lacking flagella, cingulum, and sulcus; developing food vacuole during prolonged feeding. Tomont and sporocytes without double outer membrane or cyst wall. Dinokont spores with transverse flagellum set in cingulum; longitudinal flagellum extending posteriad from sulcus.
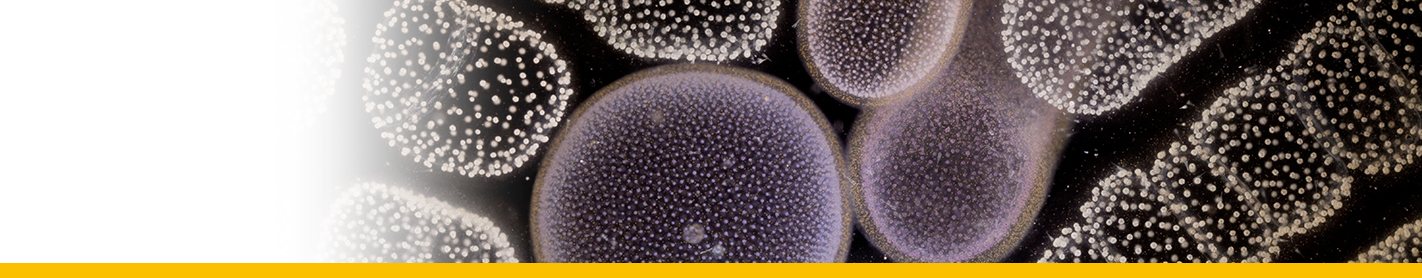
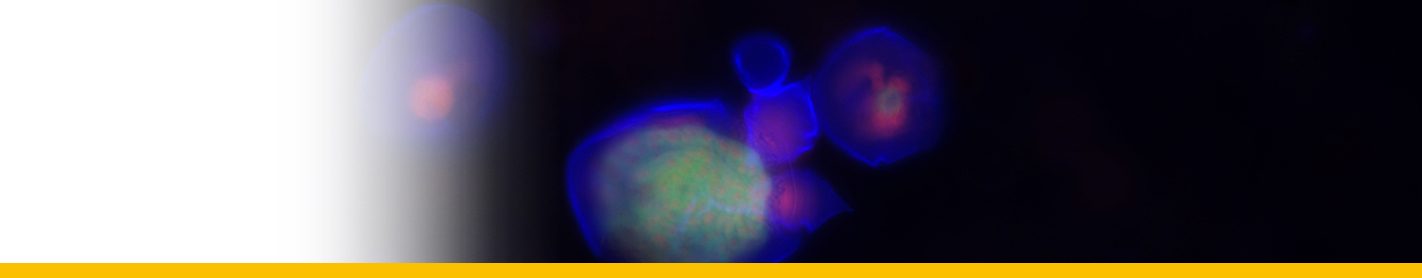
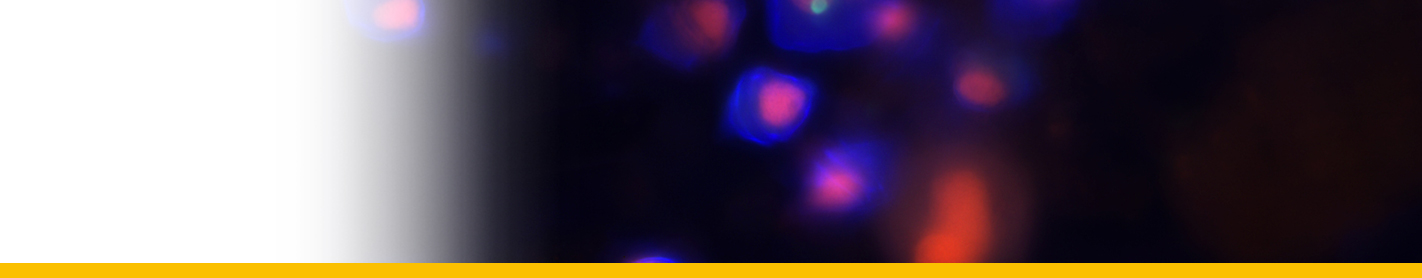
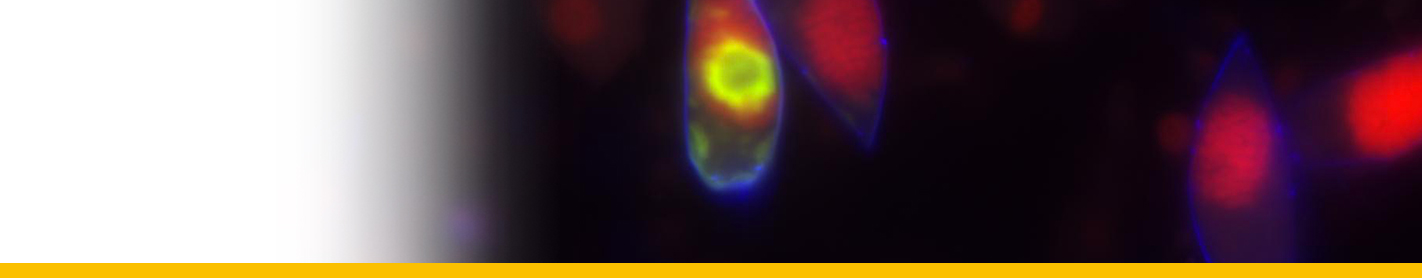
Diagnosis_Species: Duboscquella tintinnicola Lohmann, 1908, Chatton, 1920, emend. Coats & Bachvaroff 2012. Aplastidic dinospores 17--20 by 10--12 µm numbering approximately 10--24, with rounded episome and deeply cut, bi-lobed hyposome. Lacking conspicuous eyespot at base of flagella.
Body_spores_length: 17-20 µm
Body_spores_wide: 10-12 µm
Type species
This is the type species of the genus.
Type illustration / Type locality / Type specimen
Type host: Tintinnopsis nucula (now considered a species of Stenosemella, possibly S. nivalis).
Ecology
Substrate: epizoic
Salinity: marine
pH: neutral
Life cycle
Phases_alternance: haplontic
Generation: <1 month
Reproduction_mode: asexual
Symbiont: horizontal