Sargassum sp.
Diagnosis
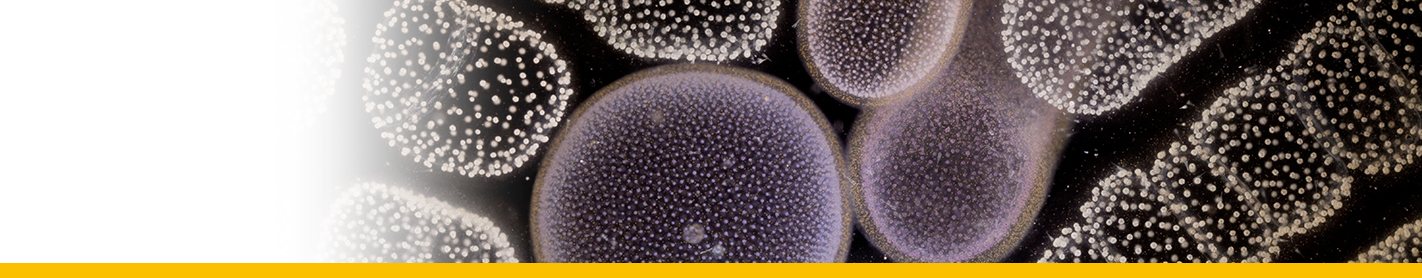
Thallus to 10-200 cm or more in length, with one to a few simple, terete to compressed, stipes 1-20 cm long arising from a discoid-conical holdfast. Stipes bearing radially or distichously borne, long primary branches, produced seasonally from the stipe apices and subsequently deciduous, leaving scars or other residues on the stipe. Primary branches 10 cm to 200 cm or more long, distichously, tristichously or radially branched with a terete, angular, compressed or three-sides axes; basal laterals simple or branched, compressed and relatively narrow to (in most species) leaf-like, (1-)3-15(-25) mm broad, entire ot with dentate margins; upper laterals usualy branched, with slender, compressed to terete, ramuli. Air bladders (vesicles) normally present, subspherical to ovoid, petiolate, mutic or apiculate, replacing ramuli or axilliary to the laterals. Growth from a 3-sided cell in an apical depression. Structure of a central medulla of elonagate cells in the stipe and branch axes, with a core of isodiametric cells and a surface of phaeoplastic meristoderm, active in the larger branched. Reproduction. Thallus monoecious or dioecious. Receptacles unisexual or bisexual, developed in axils of laterals or ramuli, simple or usually in branched clusters, terete or compressed, smooth, verrucose or spinous, with scattered conceptacles and ostioles, growing apically with conceptacles maturing below; conceptacles unisexual or bisexual.
Type species
Type specimen : Sargassum bacciferum (Turner) C.Agardh