Hematodinium-species complex
Diagnosis
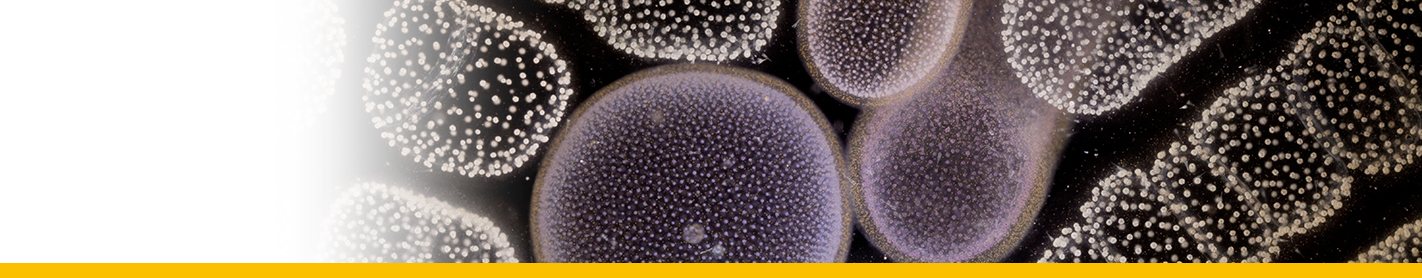
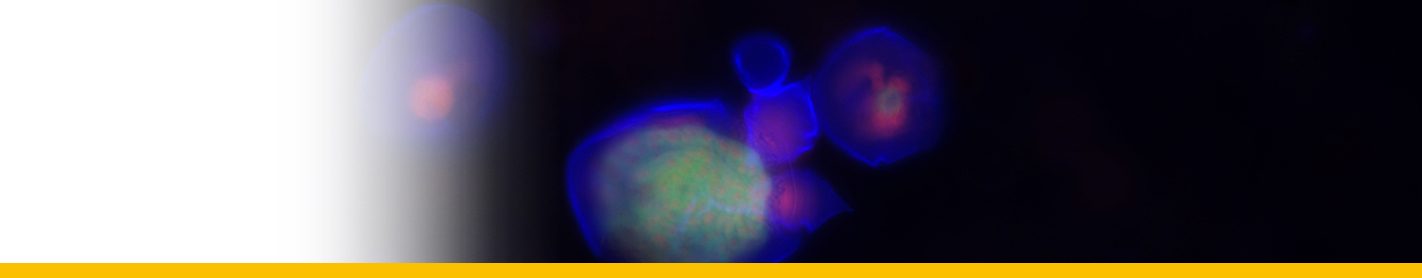
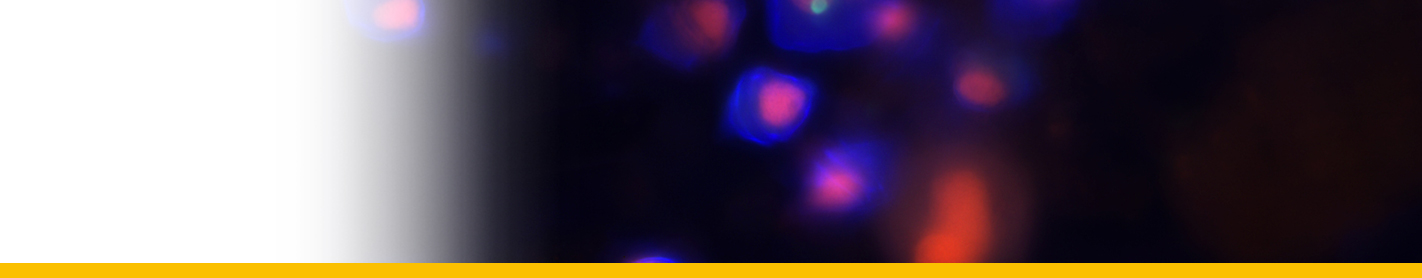
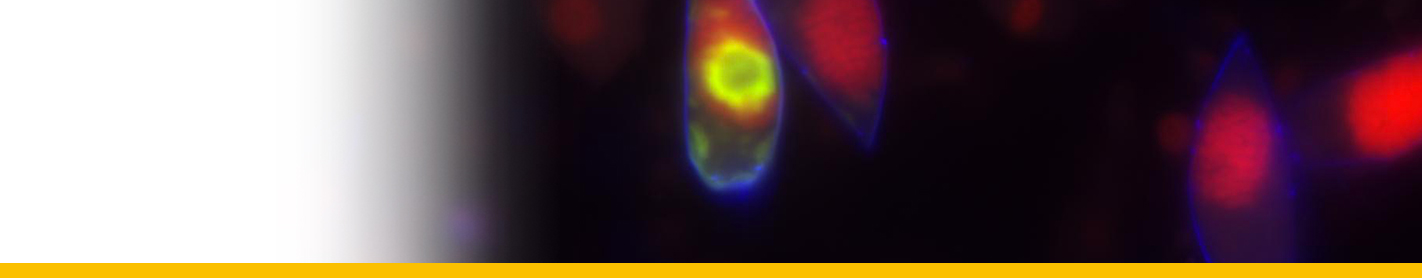
Diagnosis_Genus: The generic characters of Hematodinium are the amphiesmal structure of the pellicle, the condensed and beaded chromatin that forms V-shaped configurations of the chromosomes, the plasmodial nature of the meront, the continuous state of mitotic activity in the nucleus and the type of mitosis exhibited (dinomitosis) (Chatton & Poisson 1931, Newman & Johnson 1975, Cachon & Cachon 1987). Parasitic dinoflagellates responsable for the bitter crab syndrome (BCS, Meyers et al. 1987), named because of the bitter or astringent flavour the parasite imparts to cooked crab meat. Crabs infected by this parasite exhibit a spectrum of disease ranging from asymptomatic carriage to death. Affected hosts undergo dramatic pathological alterations to their organs, tissues, and haemolymph. Respiratory dysfunction results in lethargy, and eventual death.
Diagnosis_Species: SSU and ITS allows the separation of two species: H. perezi (called Clade A) and a undescribed species called Hematodinium sp. Clade B. Both species are coufounded by classical microscopic techniques. When molecular characterization is absent, the parasite is included in a larger group regrouping at leats these two species (Hematodinium-species complex).
Type species
The type species of this genus is H. perezi Chatton & Poisson 1931
Ecology
Substrate_trophont: endozoic
Substrate_trophont: extracellular
Substrate_spores: planktonic