Euduboscquella caryophaga
Diagnosis
Diagnosis_Genus: Euduboscquella Coats & Bachvaroff 2012. Euduboscquellidae with trophont episome as disc-shaped shield bordered by a perinematic ring. Lamina pharyngea extending from perinematic ring into trophont cytoplasm. Food vacuole formed as trophont emerges from host giving rise to extracellular tomont. Multiple spore morphotypes possible, including dinokont and non-dinokont cells. Individual infections producing only one type of spore.
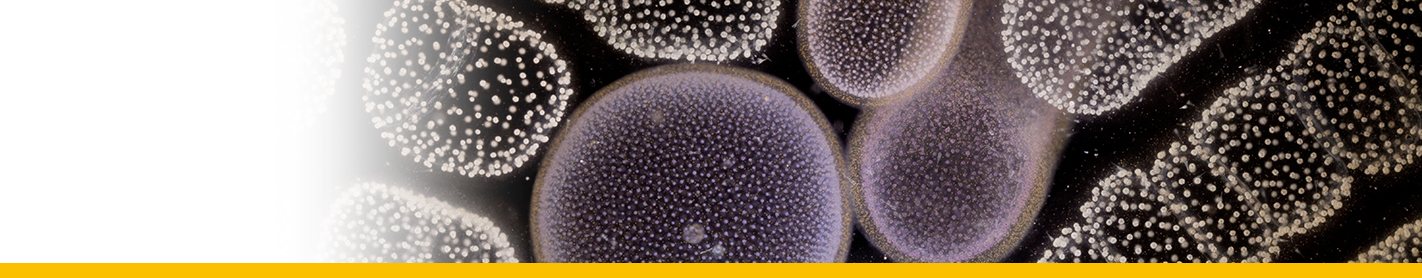
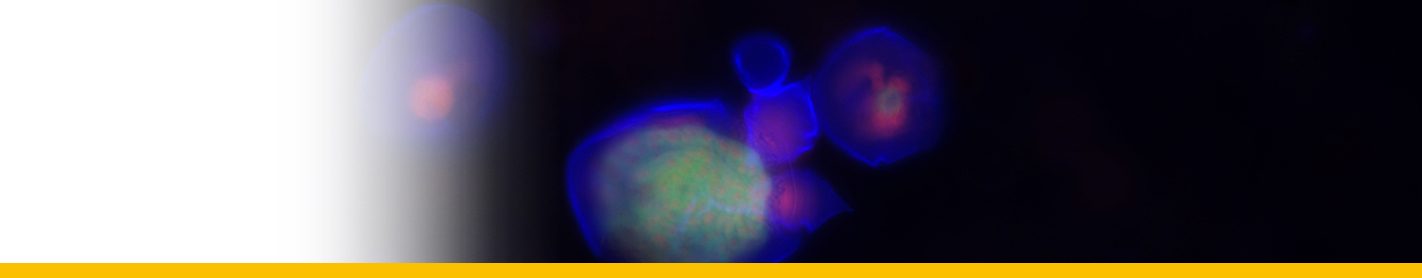
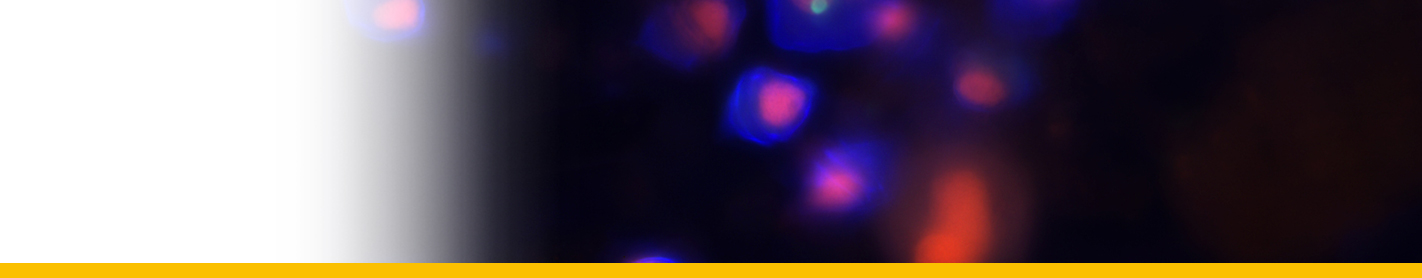
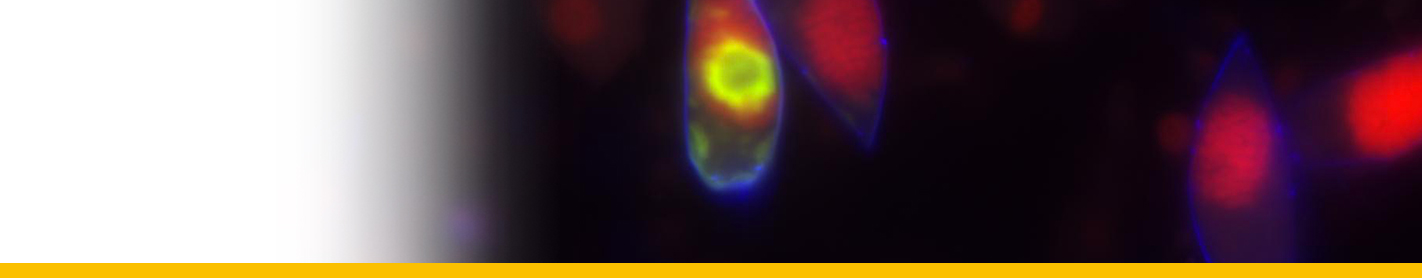
Diagnosis_Species:Trophont morphology/development: The trophont first attachs to the macronucleus of its host and digests it. Mature trophont is spherical, ~30 µm diam.; during growth, the parasite digests host’s nucleus ; the shield ressembles that of E. cnemata but only has ~10 grooves; lamina pharyngea reduced to a twisted filament; nucleolus absent in trophonts > 15 µm.
Sporogenesis: Unknown; presumed to occur outside the host.
Spore morphology: Unknown.
Body_trophont_length: 30 µm
Etymology
Genus name is derived from the Greek eu- (= well, normal) and the genus name Duboscquella.
caryophaga: digests first the host macronucleus.
Type species
The type species for the genus is E. crenulata.
Type illustration / Type locality / Type specimen
Type host: Infects Strombidium, Strombilidium and Prorodon.
Ecology
Substrate_trophont: endozoic (endoparasite)
Substrate_tomont: extracellular
Substrate_spores: planktonic
Salinity: marine
Salinity: brackish
Salinity: variable
Life cycle
Phases_alternance: haplontic
Generation: <1 month
Reproduction_mode: asexual
Symbiont: horizontal