Syndinium belari
Diagnosis
Diagnosis_Genus: These parasites were initially confounded with a putative formation of anisospores during sexual reproduction of radiolarian by Hertwig 1879 and Brandt 1885. Chatton 1923 erected a new genus (Merodinium) for all Syndinium-like parasites infesting radiolarian, then separating parasites of copepods from the ones infecting radiolarian. This separation is based on the mode of infection (intracellular in Merodinium and in the general cavity of copepods), by the earlier fragmentation of the plasmodium in Merodinium, and the shape of their spores (fusiform in Syndinium and piriform for Merodinium). Hollande and Enjumet 1953 kept the genus name Syndinium for all parasites of radiolarian located inside the capusle, and reserved the genus name of Merodinium for all extracapsular parasites. Merodinium and Syndinium were considered as synonymous two years after by Hollande and Enjumet 1955. Delineation of these two genera, if valid, needs to be more studied. Species were mainly separated based upon the identity of their host species.
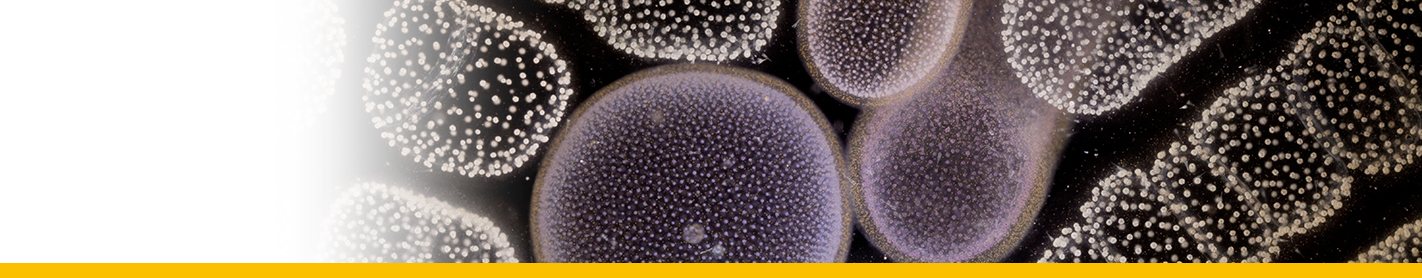
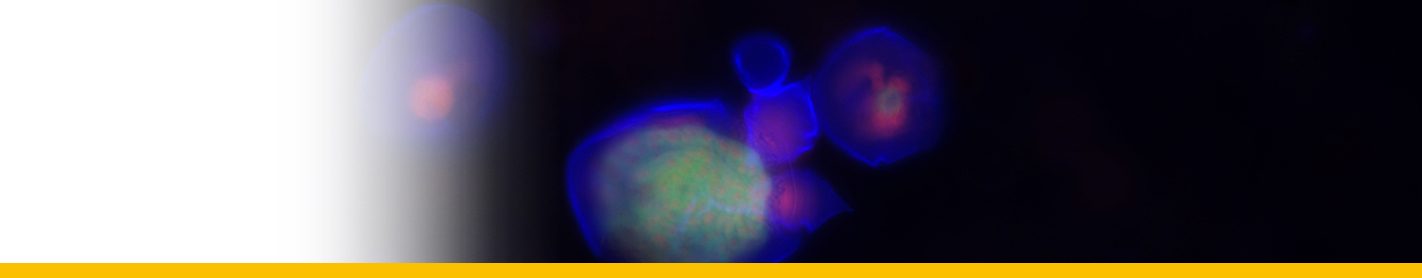
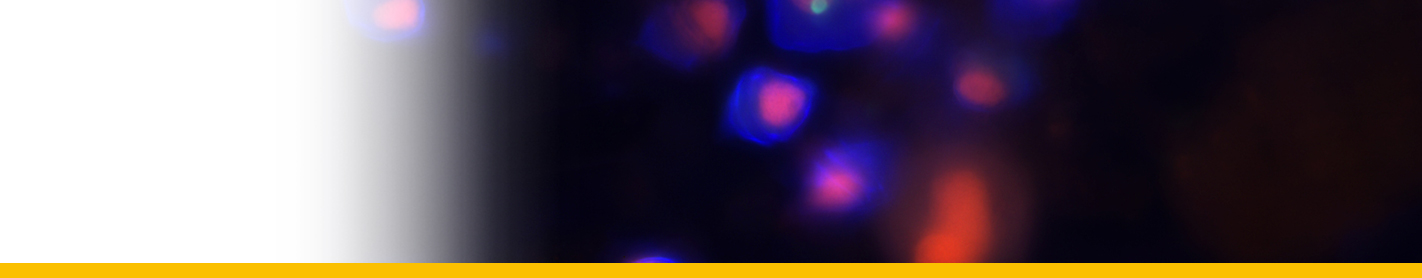
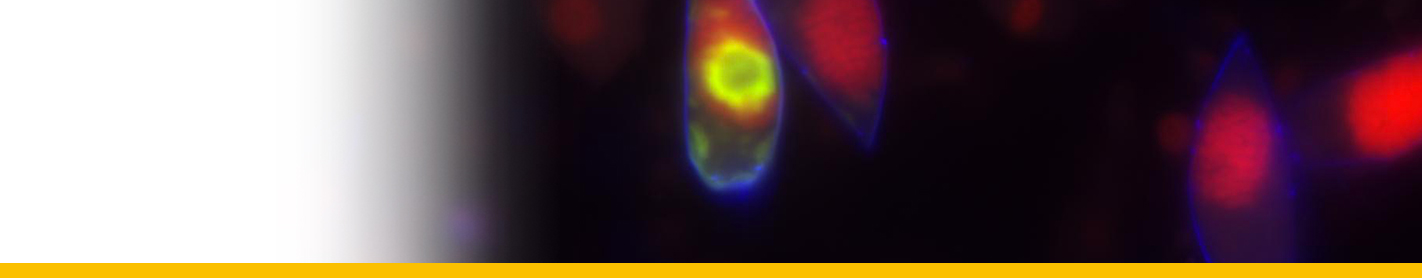
Diagnosis_Species: S. belari Hollande & Enjumet 1953. Extracapsular parasite of Collozoum fulvum. First stage uninucleated, arranged around the capsule. Infected individual host rapidly becomes opaque. The trophont nucleus is peripherical, a protruding and rapidly growing food vacuole is observed, that contain numerous lipidic granules. Two type of plasmodium are observed: 1) multinucleated (nuclei having 7 µm of diameter): the nucleus divided, forming distorted plasmodium, each of them having 4-8 to 32-64 nuclei, then fragmented into 1-2 nucleated indivuduals (uninucleated individuals sometime divided again), 2) paucinucleated (large piriform nucleus with 13 µm of diameter): separation by transversal division of the plasmodium following the nucleus division, and sometime direct sporogenesis. Divisions are almost synchrone. V-shaped chromosomes during sporogenesis (5 in total). Two type of spores are produced simultaneously (macro and microspores). Macrospores are formed by paucinucleated plasmodia (sometime not produced) and have 17 µm long. Microspores are formed by multinucleated sporonts and have 9 µm long. They contain both abundant lipidic inclusions, and at the posterior pole, they have a refringent body. Both type of spores may be able to infest a new host. Released of spores is linked with the lysis more or less partial of the host colony.
Body_microspores: 9 µm
Body_macrospores: 17 µm
Etymology
belari: In honour of Pr. Belari, who reported this parasite in 1926.
Type illustration / Type locality / Type specimen
Type host: Collozoum fulvum
Type locality: Alger bay
Ecology
Substrate: endozoic
Salinity: marine
Life cycle
Phases_alternance: haplontic (5 chromosomes, only one nucleole)
Generation: <1 month
Reproduction_mode: asexual
Symbiont: horizontal
Feeding behaviour
Mode of locomotion
Reference(s)
Observation site(s)
HOSTS
| Association with... | Region origin | Name of site | In reference... |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collozoum fulvum | Alger Bay |
(1953) Contribution à l'étude biologique des Shaerocollides (radiolaires collodaires et radiolaires polycyttaires) et de leurs parasites. Partie I.- Thalassicollidae, Physematidae, Thalassophysidae. . Ann. Sci. Nat. Zool. 11eme série:405-437. |