|
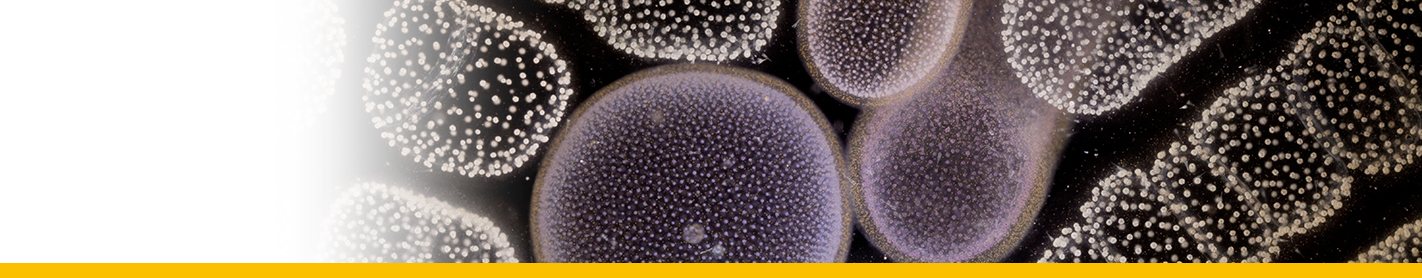
Discosoma unguja |
Gulf of Aqaba |
|
B. Kuguru, Chadwick, N. E., Achituv, Y., Zandbank, K., and Tchernov, D., “Mechanisms of habitat segregation between corallimorpharians: photosynthetic parameters and Symbiodinium types”, Marine Ecology Progress Series, vol. 369, pp. 115 - 129, 2008. |
|
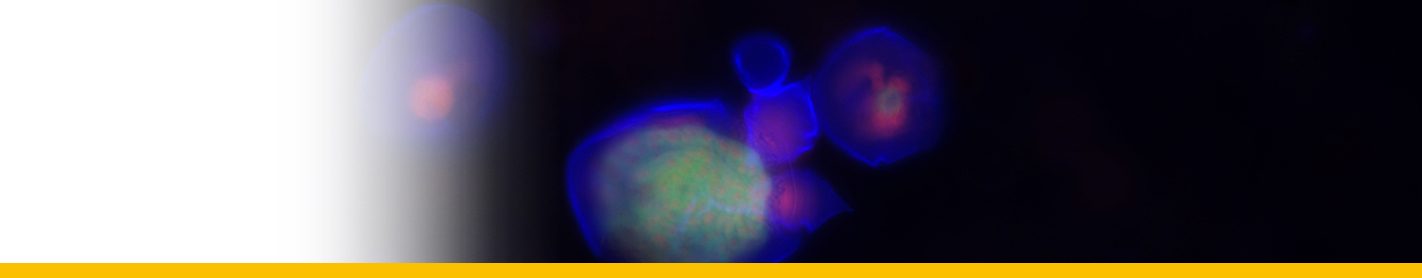
Discosoma unguja |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
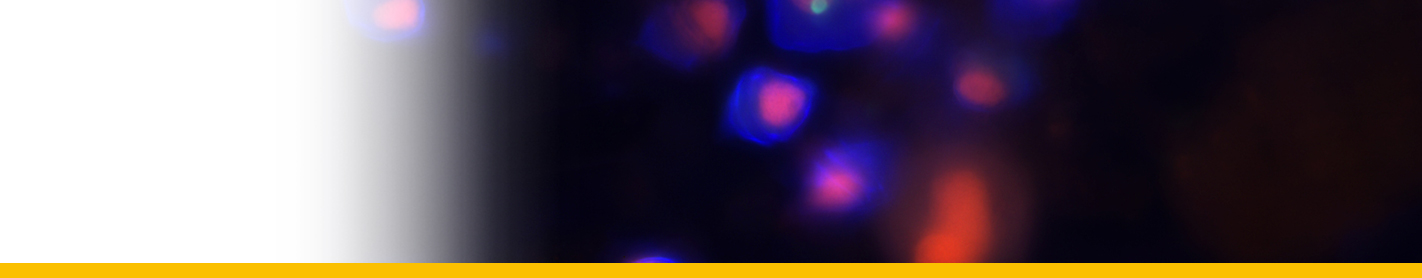
Discosoma unguja |
Gulf of Aqaba |
|
B. Kuguru, Chadwick, N. E., Achituv, Y., Zandbank, K., and Tchernov, D., “Mechanisms of habitat segregation between corallimorpharians: photosynthetic parameters and Symbiodinium types”, Marine Ecology Progress Series, vol. 369, pp. 115 - 129, 2008. |
|
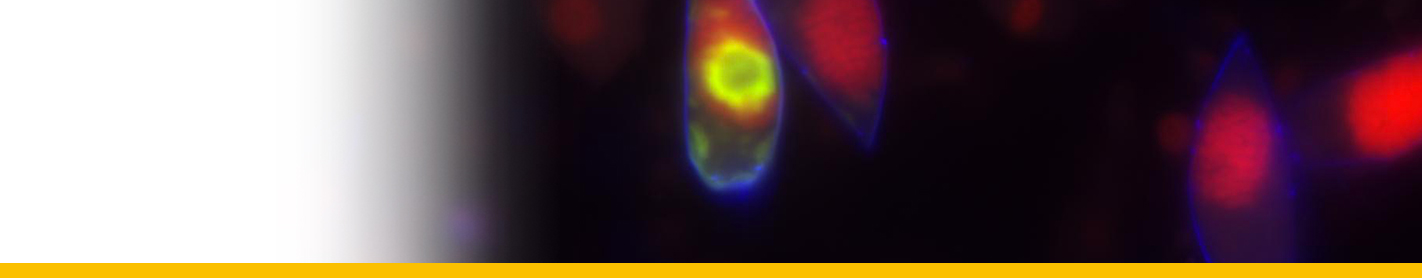
Discosoma unguja |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Discosoma unguja |
Gulf of Aqaba |
|
B. Kuguru, Chadwick, N. E., Achituv, Y., Zandbank, K., and Tchernov, D., “Mechanisms of habitat segregation between corallimorpharians: photosynthetic parameters and Symbiodinium types”, Marine Ecology Progress Series, vol. 369, pp. 115 - 129, 2008. |
|
Discosoma unguja |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Discosoma unguja |
Gulf of Aqaba |
|
B. Kuguru, Chadwick, N. E., Achituv, Y., Zandbank, K., and Tchernov, D., “Mechanisms of habitat segregation between corallimorpharians: photosynthetic parameters and Symbiodinium types”, Marine Ecology Progress Series, vol. 369, pp. 115 - 129, 2008. |
|
Erythropodium caribaeorum |
Eastern Caribbean |
|
C. J. Finney, Pettay, D. Tye, Sampayo, E. M., Warner, M. E., Oxenford, H. A., and LaJeunesse, T. C., “The Relative Significance of Host–Habitat, Depth, and Geography on the Ecology, Endemism, and Speciation of Coral Endosymbionts in the Genus Symbiodinium”, Microbial Ecology, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 250 - 263, 2010. |
|
Erythropodium caribaeorum |
Eastern Caribbean |
|
C. J. Finney, Pettay, D. Tye, Sampayo, E. M., Warner, M. E., Oxenford, H. A., and LaJeunesse, T. C., “The Relative Significance of Host–Habitat, Depth, and Geography on the Ecology, Endemism, and Speciation of Coral Endosymbionts in the Genus Symbiodinium”, Microbial Ecology, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 250 - 263, 2010. |
|
Erythropodium caribaeorum |
Western Caribbean |
|
C. J. Finney, Pettay, D. Tye, Sampayo, E. M., Warner, M. E., Oxenford, H. A., and LaJeunesse, T. C., “The Relative Significance of Host–Habitat, Depth, and Geography on the Ecology, Endemism, and Speciation of Coral Endosymbionts in the Genus Symbiodinium”, Microbial Ecology, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 250 - 263, 2010. |
|
Erythropodium caribaeorum |
Western Caribbean |
|
C. J. Finney, Pettay, D. Tye, Sampayo, E. M., Warner, M. E., Oxenford, H. A., and LaJeunesse, T. C., “The Relative Significance of Host–Habitat, Depth, and Geography on the Ecology, Endemism, and Speciation of Coral Endosymbionts in the Genus Symbiodinium”, Microbial Ecology, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 250 - 263, 2010. |
|
Erythropodium caribaeorum |
Quintana Roo |
|
T. LaJeunesse, “Diversity and community structure of symbiotic dinoflagellates from Caribbean coral reefs”, Marine Biology, vol. 141, no. 2, pp. 387 - 400, 2002. |
|
Eunicea sp. |
Western Caribbean |
|
C. J. Finney, Pettay, D. Tye, Sampayo, E. M., Warner, M. E., Oxenford, H. A., and LaJeunesse, T. C., “The Relative Significance of Host–Habitat, Depth, and Geography on the Ecology, Endemism, and Speciation of Coral Endosymbionts in the Genus Symbiodinium”, Microbial Ecology, vol. 60, no. 1, pp. 250 - 263, 2010. |
|
Eunicea sp. |
Florida |
|
S. R. Santos, Taylor, D. J., and Coffroth, M. Alice, “GENETIC COMPARISONS OF FRESHLY ISOLATED VERSUS CULTURED SYMBIOTIC DINOFLAGELLATES: IMPLICATIONS FOR EXTRAPOLATING TO THE INTACT SYMBIOSIS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 900 - 912, 2001. |
|
Eunicea tourneforti |
Quintana Roo |
|
T. LaJeunesse, “Diversity and community structure of symbiotic dinoflagellates from Caribbean coral reefs”, Marine Biology, vol. 141, no. 2, pp. 387 - 400, 2002. |
|
Eunicea ciavigera |
Quintana Roo |
|
T. LaJeunesse, “Diversity and community structure of symbiotic dinoflagellates from Caribbean coral reefs”, Marine Biology, vol. 141, no. 2, pp. 387 - 400, 2002. |
|
Eunicea mammosa |
Exuma Islands |
|
T. LaJeunesse, “Diversity and community structure of symbiotic dinoflagellates from Caribbean coral reefs”, Marine Biology, vol. 141, no. 2, pp. 387 - 400, 2002. |
|
Fragum unedo |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Fragum unedo |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Haliclona sp. |
Heron Island |
Coral Gardens |
M. J. Garson, Flowers, A. E., Webb, R. I., Charan, R. D., and McCaffrey, E. J., “A sponge/dinoflagellate association in the haplosclerid sponge Haliclona sp.: cellular origin of cytotoxic alkaloids by Percoll density gradient fractionation”, Cell and Tissue Research, vol. 293, no. 2, pp. 365 - 373, 1998. |
|
Haliclona koremella |
|
|
X. Pochon, Garcia-Cuetos, L., Baker, A. C., Castella, E., and Pawlowski, J., “One-year survey of a single Micronesian reef reveals extraordinarily rich diversity of Symbiodinium types in soritid foraminifera”, Coral Reefs, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 867 - 882, 2007. |
|
Heteractis aurora |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis crispa |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis crispa |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis crispa |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis crispa |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis magnifica |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis magnifica |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis magnifica |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis magnifica |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis magnifica |
Phuket |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Heteractis magnifica |
Great Barrier Reef |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Loh, W. K. W., van Woesik, R., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., Schmidt, G. W., and Fitt, W. K., “Low symbiont diversity in southern Great Barrier Reef corals, relative to those of the Caribbean”, Limnology and Oceanography, vol. 48, no. 5, pp. 2046 - 2054, 2003. |
|
Heteractis magnifica |
Great Barrier Reef |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Bhagooli, R., Hidaka, M., deVantier, L., Done, T., Schmidt, G. W., Fitt, W. K., and Hoegh-Guldberg, O., “Closely related Symbiodinium spp. differ in relative dominance in coral reef host communities across environmental, latitudinal and biogeographic gradients”, Marine Ecology Progress Series, vol. 284, pp. 147 - 161, 2004. |
|
Heteractis sp. |
Phuket |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, “INVESTIGATING THE BIODIVERSITY, ECOLOGY, AND PHYLOGENY OF ENDOSYMBIOTIC DINOFLAGELLATES IN THE GENUS SYMBIODINIUM USING THE ITS REGION: IN SEARCH OF A "SPECIES" LEVEL MARKER”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 866 - 880, 2001. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, “INVESTIGATING THE BIODIVERSITY, ECOLOGY, AND PHYLOGENY OF ENDOSYMBIOTIC DINOFLAGELLATES IN THE GENUS SYMBIODINIUM USING THE ITS REGION: IN SEARCH OF A "SPECIES" LEVEL MARKER”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 866 - 880, 2001. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus hippopus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus porcellanus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Hippopus porcellanus |
|
|
B. K. Baillie, Belda-Baillie, C. A., and Maruyama, T., “CONSPECIFICITY AND INDO-PACIFIC DISTRIBUTION OF SYMBIODINIUM GENOTYPES (DINOPHYCEAE) FROM GIANT CLAMS”, Journal of Phycology, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1153 - 1161, 2000. |
|
Lemnalia sp. |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |
|
Lemnalia sp. |
Western Indian |
|
T. C. LaJeunesse, Pettay, D. T., Sampayo, E. M., Phongsuwan, N., Brown, B., Obura, D. O., Hoegh-Guldberg, O., and Fitt, W. K., “Long-standing environmental conditions, geographic isolation and host-symbiont specificity influence the relative ecological dominance and genetic diversification of coral endosymbionts in the genus Symbiodinium”, Journal of Biogeography, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 785 - 800, 2010. |